How Chile’s Article 6 regulation will unlock international carbon finance
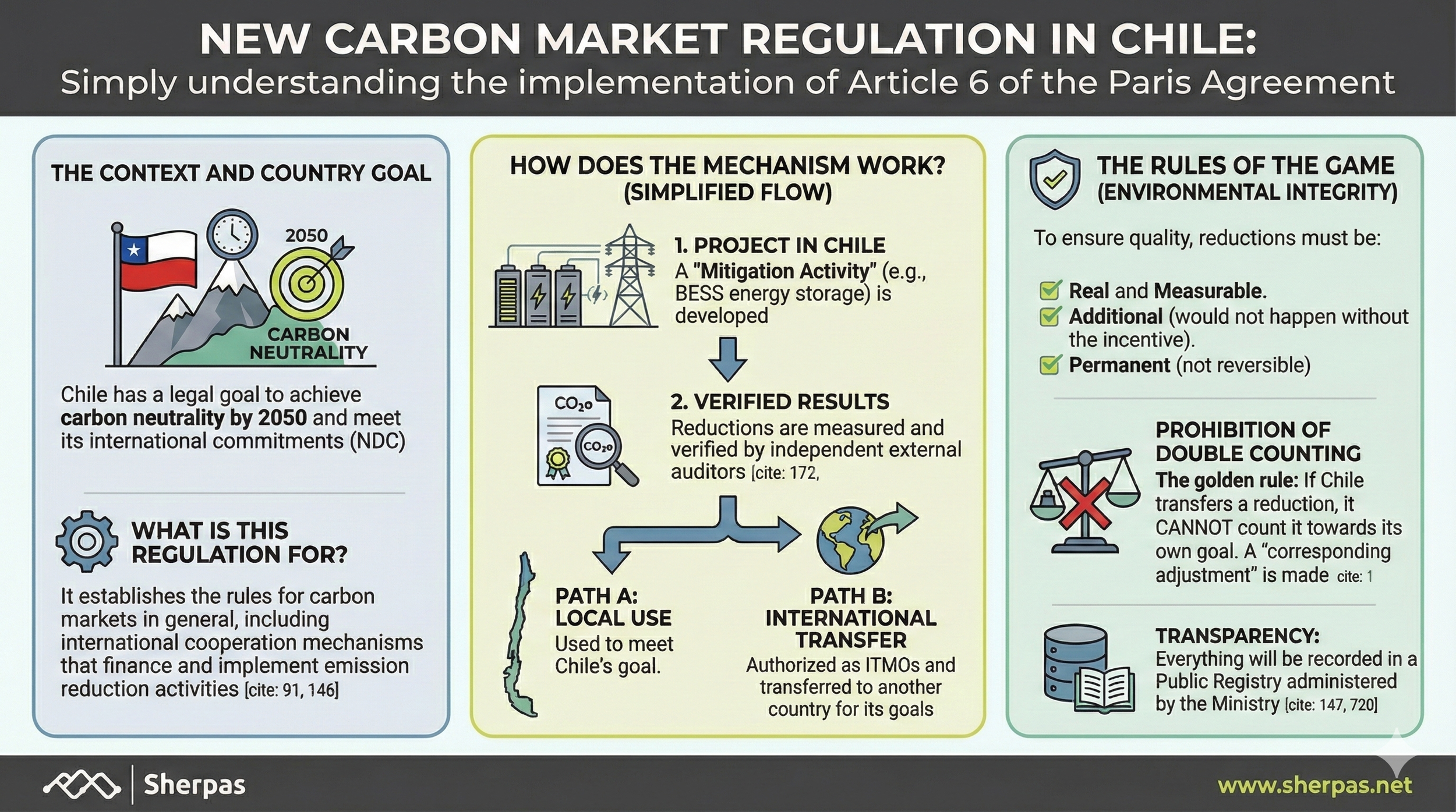
Chile’s Ministerio del Medio Ambiente has approved the regulation setting conditions for emission reduction and removal certificates under the Article 6 cooperation mechanisms of the Paris Agreement. The new rules support Chile’s 2050 carbon‑neutrality goal and provide a clear legal framework for domestic and international carbon markets.
The regulation outlines a simple process: a mitigation activity – such as a battery‑energy‑storage project or other climate initiative – is implemented, its results are measured and verified by independent auditors, and the certified reductions can then be used domestically to meet Chile’s nationally determined contribution (#NDC) or transferred internationally as Internationally Transferred Mitigation Outcomes (#ITMOs), linking local action with global carbon finance.
To guarantee integrity, all outcomes must be real, additional, measurable, verified, and permanent—only genuine, non‑reversible reductions qualify. The decree also bans double-counting by preventing double issuance, double claims, and double use of certificates, and it creates a public national registry to track authorised entities, methodologies, projects, and verified results.
Together, these measures position Chile at the forefront of climate policy, enabling high‑integrity carbon projects and ensuring that each tonne of avoided or removed CO₂ counts only once. See the attached infographic for a simplified overview of the mechanism and prepare for a more transparent, accountable carbon market.